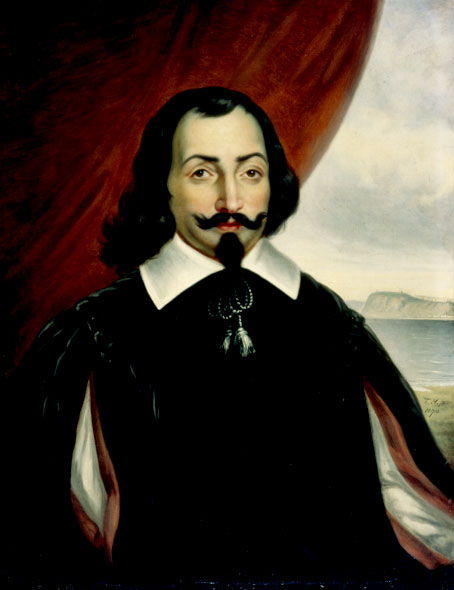
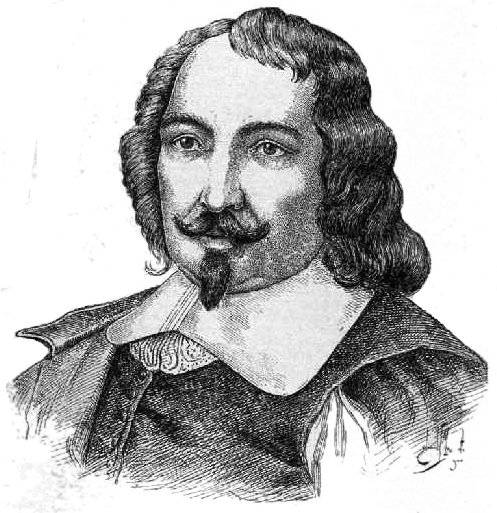
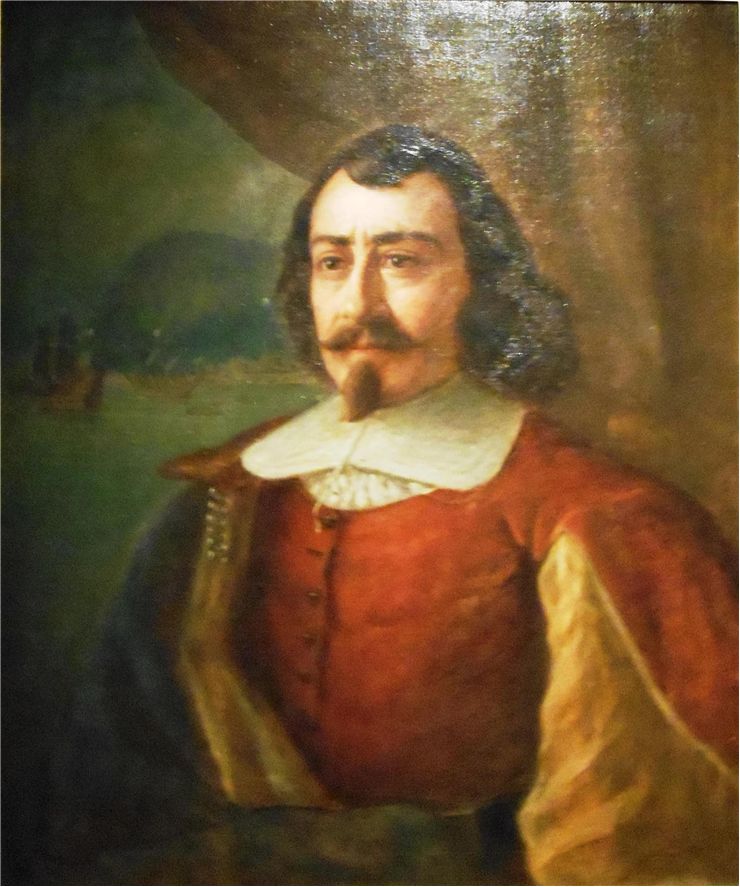
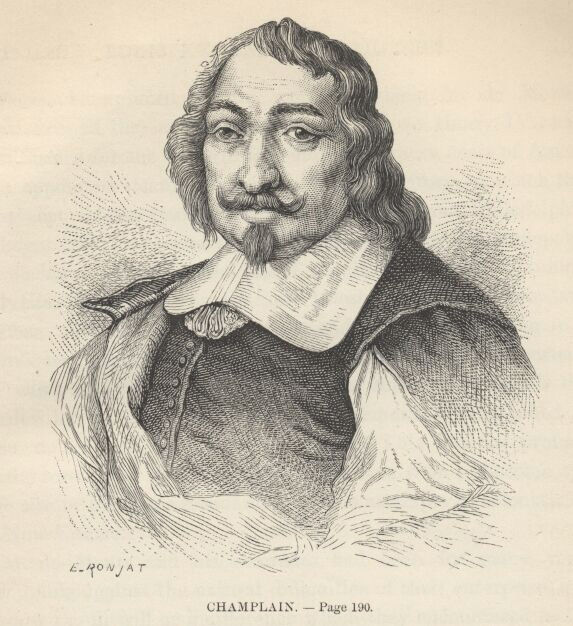
Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain (1567 – 1635) was one of the most famous French explorers of the 17th century and a man who spearheaded French expansion to Canada and formation of the Quebec City in 1608. For his contributions he is today remembered as one of the most important figures in the Canadian history, often being named "The Father of New France" or “The Father of Canada”.
Samuel de Champlain was born on August 13, 1574 (some historians speculate it was little earlier) at Brouage, Saintonge in France as a son of sea mariner Antoine Champlain and his wife Marguerite Le Roy. During his entire youth Samuel learned about life at sea by following his father and uncle on sea journeys, and was well educated in cartography, navigation, astronomy and mathematics. In 1587 he joined French army and eventually reached the rank of quartermaster of cavalry. However, in 1598 he managed to finally reach posting of the sea when he started working on the support fleet of his uncle who was Pilot-General of Spanish Army (Spanish and French were allies in the fight against England). During the same year Samuel received invitation to lead a ship to a new world as a part of a larger Spanish fleet.
After spending three years in the Caribbean observing vast Spanish holdings between 1599 and 1602, Samuel de Champlain returned to France where he was welcomed warmly and named as “Geographer to the King”. The following 18 years of his life then became one of the most famous periods of time for Spanish exploration in the early years of 17th century. Samuel de Champlain explored North America with François Gravé Du Pont in 1603, explored and transferred French settlers to one of the New France’sfirst cities Port Royal, Acadia between 1604 and 1607. In the following year he continued exploring northern shore of America and formedthesettlement of Quebec City, which later on became one of the most important ports for French expansion to the North America and eventual formation of Canada. During his period in Quebec City, Champlain explored much of the Great Lakes and managed to extract a lot of unknown information from the native Indians that lived in those lands. Indian tribes that lived near Quebec formed a good relations with the French, which would later on play a big role with the arrival of several wars that were fought in that area.
In 1620, Champlain’s life of exploration finally came to the end when he received official orders from French king Louis XIII to return to Quebec City where he will continue to serve government as Governor of New France. He remained on that position until the 1535 when he died from stroke.
Samuel de Champlain is today remembered as one of the greatest pioneers of French expansion in the 17th century. By forming several settlements (most notably Acadia and Quebec City), and exploring much of the Great Lakes, he enabled France to get a firm grip on the north American continent and form the modern country of Canada. Today, his name can be found on countless memorials, landmarks and public spaces in Canada.
| Name | Samuel de Champlain |
| Born | Baptised August 13, 1574 |
| Place of Birth | Brouage or La Rochelle, Aunis, France |
| Died | December 25, 1635 |
| Place of Death | Quebec City, Canada |
| Category (Occupation/Profession) | navigator, cartographer, soldier, explorer, administrator and chronicler of New France |
| Nationality | French |
| Religion | Catholic |
| Known For | Foundation of Quebec City, Canada, being called The Father of New France |
| Famous Expedition(s) | Exploration of New France |
| Spouse(s) | Hélène Boullé |
| Children | Faith, Hope, Charity |
| Parent(s) | Antoine Champlain, Marguerite Le Roy |
| Monuments | Sir Sandford Fleming Park, Halifax, Nova Scotia |